Maternal mortality rates represent a critical and alarming challenge within the sphere of public health, especially in the United States, where these rates have been on a troubling rise. Over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable, yet systemic issues in healthcare contribute to persistent disparities across state lines and racial groups. The latest research indicates that conditions like cardiovascular disease in pregnancy are major contributors to these tragic outcomes, highlighting a need for enhanced maternal health initiatives. Addressing these inequities in healthcare requires not just improved access to prenatal and postpartum care but also a shift in public health policies to better support at-risk populations. As we delve deeper into the reasons behind these alarming trends, it becomes evident that immediate action is essential to safeguard the health and lives of mothers across the nation.
The discussion around maternal mortality encompasses a range of issues related to maternal deaths tied to pregnancy and childbirth complications. These fatalities, often preventable, underscore the urgency of improving healthcare support for mothers before, during, and after giving birth. With a notable focus on extended postpartum care, the conversation shifts toward transforming our understanding of maternal health through the lens of comprehensive care. In exploring the consequences of healthcare inequities, we must also consider the broader implications that various conditions, such as cardiovascular issues and other chronic diseases, have on new mothers. Ultimately, these factors illuminate the pressing need for systemic changes to protect women from the heightened risks associated with reproductive health.
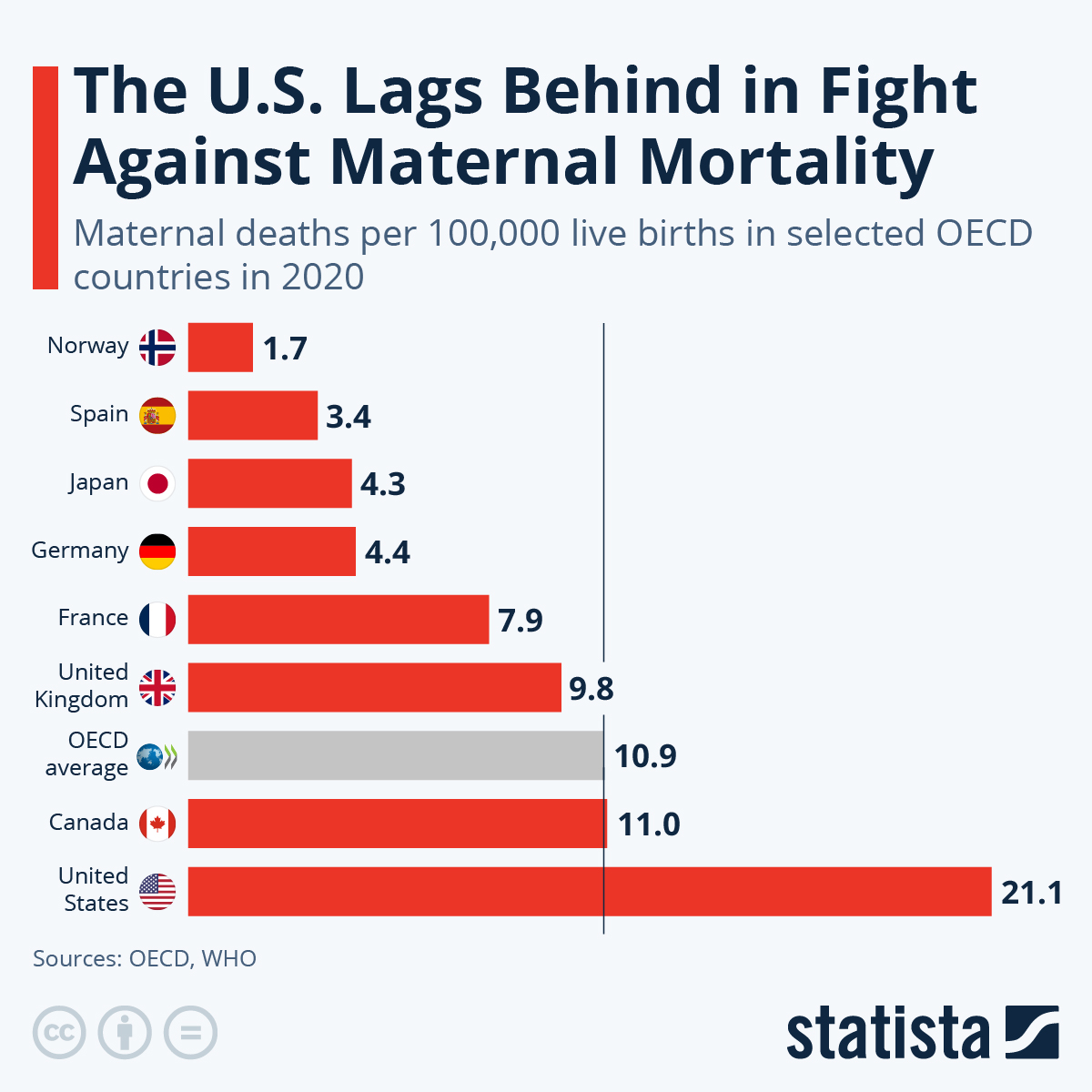
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
Maternal mortality rates in the United States are alarmingly high, with the nation leading other high-income countries in this critical health metric. According to recent studies, over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, yet the rates continue to escalate due to multifaceted issues. The complexity of the healthcare system, which often appears like a patchwork, can significantly affect access to necessary services and contribute to these preventable deaths. Additionally, socioeconomic factors and systemic inequities have made it difficult for marginalized communities to receive the maternal health care they deserve.
The persistent rise in maternal mortality rates between 2018 and 2022 highlights the urgent need for reform. Disparities across racial and ethnic lines are evident, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. Furthermore, these inequities in healthcare are exacerbated by existing policies and the lack of a coordinated approach to maternity care. Ensuring everyone receives equitable prenatal and postpartum care is essential for reducing these alarming rates.
Inequities in Healthcare and Maternal Health
Inequities in healthcare pose a significant challenge to maternal health, resulting in disproportionate outcomes for various racial and ethnic groups. The prevalence of systemic bias within the healthcare system has been documented repeatedly, indicating that improvements toward equity are not yet being realized. Addressing the underlying policies that perpetuate these inequities is crucial if the U.S. aims to lower maternal mortality rates significantly. Solutions must focus on creating a more inclusive healthcare environment that caters to the needs of all populations.
Beyond addressing disparities, it is vital to reform the broader healthcare system to eliminate ‘maternity care deserts’. Many women lack access to quality prenatal and postpartum care due to geographic and economic barriers. Although some innovations have appeared to bridge these gaps, the overall lack of improvement suggests that a shift in policy and resource allocation is necessary. Investing in targeted interventions for high-risk groups can streamline the process of reducing inequalities in maternal health, ultimately leading to healthier outcomes.
The Role of Postpartum Care in Preventing Maternal Deaths
Postpartum care often receives less attention in the healthcare system, yet it is a critical aspect of addressing maternal mortality. Recent findings indicate that late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and one year post-pregnancy, account for a significant percentage of overall maternal deaths. Comprehensive postpartum care extends beyond the traditional six-week checkup, promoting a continuum of care that addresses the physical and mental health needs of new mothers. By restructuring postpartum care services, healthcare providers can better anticipate and mitigate risks that contribute to death during this vulnerable period.
To improve outcomes during the postpartum phase, healthcare systems must prioritize continuous monitoring and support for postpartum women. This includes addressing chronic conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease, which have been identified as leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths. With a holistic approach to postpartum care that considers a woman’s mental health and pre-existing conditions, the healthcare system can actively work to lower maternal mortality rates and ensure that mothers are supported long after the birth of their child.
The Impact of Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., highlighting a worrying trend that reflects broader health issues in society. The increase in chronic conditions like hypertension among pregnant individuals has raised significant concerns, particularly as younger populations are now being affected more than before. Understanding why cardiovascular disease is increasingly prevalent requires an examination of lifestyle factors, healthcare access, and the overall management of women’s health throughout their reproductive years.
The rising instances of cardiovascular complications during pregnancy underscore the critical need for proactive healthcare measures. Effective screening and management of cardiovascular conditions need to be integrated into prenatal care routines. Additionally, educational programs aimed at improving awareness of cardiovascular risks among women of reproductive age could play a pivotal role in preventing these complications and ultimately reducing maternal mortality rates associated with cardiovascular disease.
Mental Health and Its Effects on Maternal Mortality
Mental health is an often-overlooked component of maternal health that can profoundly affect both maternal and child outcomes. The postpartum period is a time of increased vulnerability for mental health disorders, such as postpartum depression and anxiety. When left unaddressed, these conditions can exacerbate physical health problems and contribute to increased maternal mortality. It is fundamental for healthcare systems to incorporate mental health screenings and support as part of comprehensive maternal care.
Additionally, societal stigma around mental health can prevent women from seeking help during or after pregnancy. Reducing this stigma, alongside creating more accessible mental health resources, can significantly improve maternal health outcomes. By recognizing the connection between psychological well-being and physical health, we can develop a more effective approach to tackling high maternal mortality rates in various populations.
The Importance of Policy Changes for Maternal Health
Many of the maternal mortality challenges facing the U.S. can be traced to systemic policy failures. A patchwork of state-level healthcare policies has resulted in significant disparities in maternal health outcomes across the country. Advocating for comprehensive policy reform at the national level is crucial if we are to effectively address the high maternal mortality rates and implement interventions that close the equity gap. Policies should focus on increasing funding for maternal health programs, improving data collection on maternal deaths, and expanding access to prenatal and postpartum care.
Moreover, engaging in community-based initiatives that prioritize maternal health can enhance policy effectiveness. These initiatives can lead to better understanding and addressing the unique challenges faced by different populations. A concerted effort to refine existing healthcare policies and invest in maternal health is imperative as we work towards reducing preventable deaths and improving overall pregnancy outcomes.
Innovations in Maternal Care: Bridging the Gap
Emerging innovations in maternal care can help bridge the gap in healthcare access and quality that many women experience. Telehealth services, for instance, have gained popularity, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing women to receive prenatal and postpartum care in a more accessible manner. Such technology provides opportunities for healthcare providers to monitor risk factors effectively and ensure that patients receive timely interventions when needed, which can be life-saving.
In addition to telehealth, community-based programs that focus on education and support can empower women to take charge of their maternal health. These programs can provide resources for prenatal care, mental health support, and information on managing chronic conditions. By fostering a strong support network and increasing awareness, these innovations hold the potential to dramatically improve maternal health outcomes and significantly lower maternal mortality rates.
Tracking Maternal Deaths for Better Health Solutions
Accurate tracking and reporting of maternal deaths is vital for informing public health initiatives aimed at improving maternal health. The implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates was a crucial step toward understanding the full scope of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. However, continued enhancements to data collection processes are needed to ensure comprehensive insights into maternal mortality causes. This information can drive evidence-based policy and resource allocation to mitigate risks and enhance care options.
In line with systematic data collection, establishing a national registry for maternal deaths could further aid in identifying patterns and risk factors associated with mortality. This approach would not only improve tracking of maternal deaths but also enable better allocation of resources and targeted interventions for high-risk groups. A consistent focus on research and evidence-based practices is essential for reducing maternal mortality rates and enhancing the standard of maternal healthcare across the nation.
Community Engagement in Improving Maternal Health Outcomes
Community engagement plays a significant role in improving maternal health outcomes by ensuring that care meets the needs of diverse populations. Local initiatives that involve women in the decision-making processes around maternal health can empower communities. These programs create awareness about available resources and educational opportunities that can lead to informed healthcare choices and enhanced support systems during pregnancy and beyond.
Furthermore, involving community leaders in maternal health discussions can help tailor interventions to fit specific cultural and socioeconomic contexts. This localized approach not only builds trust within the community but also encourages women to seek care proactively. By prioritizing community engagement, healthcare systems can effectively reduce maternal mortality rates and improve the overall maternity care experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current maternal mortality rates in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income countries, with 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, rising from 25.3 deaths in 2018. This stark contrast highlights serious inequities in healthcare and the need for improved maternal health policies.
How can we address rising pregnancy-related deaths and improve maternal health in the U.S.?
To tackle rising pregnancy-related deaths, it’s crucial to invest in comprehensive healthcare infrastructure targeting maternal health. This includes improving prenatal care, addressing postpartum care gaps, and implementing policies to reduce inequities in healthcare that affect maternal mortality rates.
What role does cardiovascular disease play in maternal mortality rates?
Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for over 20% of such deaths. The increase in chronic conditions like hypertension in younger populations contributes significantly to rising maternal mortality rates.
What are the disparities in maternal mortality rates among different racial and ethnic groups?
Significant disparities exist in maternal mortality rates across racial and ethnic lines, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing a mortality rate of 106.3 per 100,000 live births—nearly four times higher than that of white women. Addressing these inequities is vital for improving overall maternal health.
Why is postpartum care critical in reducing maternal mortality rates?
Postpartum care is essential for reducing maternal mortality rates because nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy. By extending healthcare support beyond the traditional six-week postpartum period, we can better monitor and improve maternal health outcomes.
What can be done to reduce inequities in maternal health outcomes?
To reduce inequities in maternal health outcomes, we must implement targeted policies that address healthcare access, improve quality of care in underserved communities, and increase public health funding. This can help minimize the disparities in maternal mortality rates across different states and populations.
How do pregnancy-related deaths impact maternal health discussions in the U.S.?
The rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths emphasize the urgent need for systemic change in maternal health discussions. They highlight the importance of prioritizing women’s health and investing in research to inform better policies that can improve maternal mortality rates.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, which has been rising since 2018. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable with better healthcare. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | 2021 saw a sharp increase in maternal mortality likely linked to the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Disparities Among Races | Significant disparities exist: American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest mortality rates. |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, indicating a shift from previous causes. |
| Need for System Improvements | A comprehensive healthcare reform is essential to improve maternal health and address inequities. |
Summary
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. present a significant public health crisis, exhibiting alarming trends that necessitate urgent attention. Despite advances in medicine, the nation continues to lead among high-income countries with the highest rates of maternal mortality, predominantly due to preventable causes. Addressing systemic issues within healthcare, particularly regarding access and quality of care across diverse populations, is crucial in reducing these rates and improving overall maternal health outcomes.