Is sugar addictive? This pressing question has sparked heated debates among nutrition experts, particularly as society grapples with rampant sugar cravings linked to processed foods. While sugar doesn’t officially classify as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, its ability to trigger compulsive eating behaviors can certainly feel addictive. The effects of sugar on the brain create a cycle of desire that many find challenging to resist, often leading to increased added sugar consumption. Understanding the health effects of sugar is vital, as it impacts how we perceive our cravings and can influence dietary choices.
The allure of sweetness in our diets is a topic surrounded by various alternative descriptors such as sugar obsession and sweet cravings. These terms encapsulate the complex relationship people have with sugary foods, which can lead to patterns similar to substance dependency. When exploring the impact of carbohydrates, particularly refined sugars, it becomes clear that individuals may experience not just physical cravings but also psychological dependencies that mimic those found in true addictions. Investigating the extensive health ramifications surrounding sugar intake is pivotal to understanding its influence on daily nutrition. As we examine food habits, addressing issues like sugar fixation can promote healthier choices and awareness about our consumption patterns.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Implications
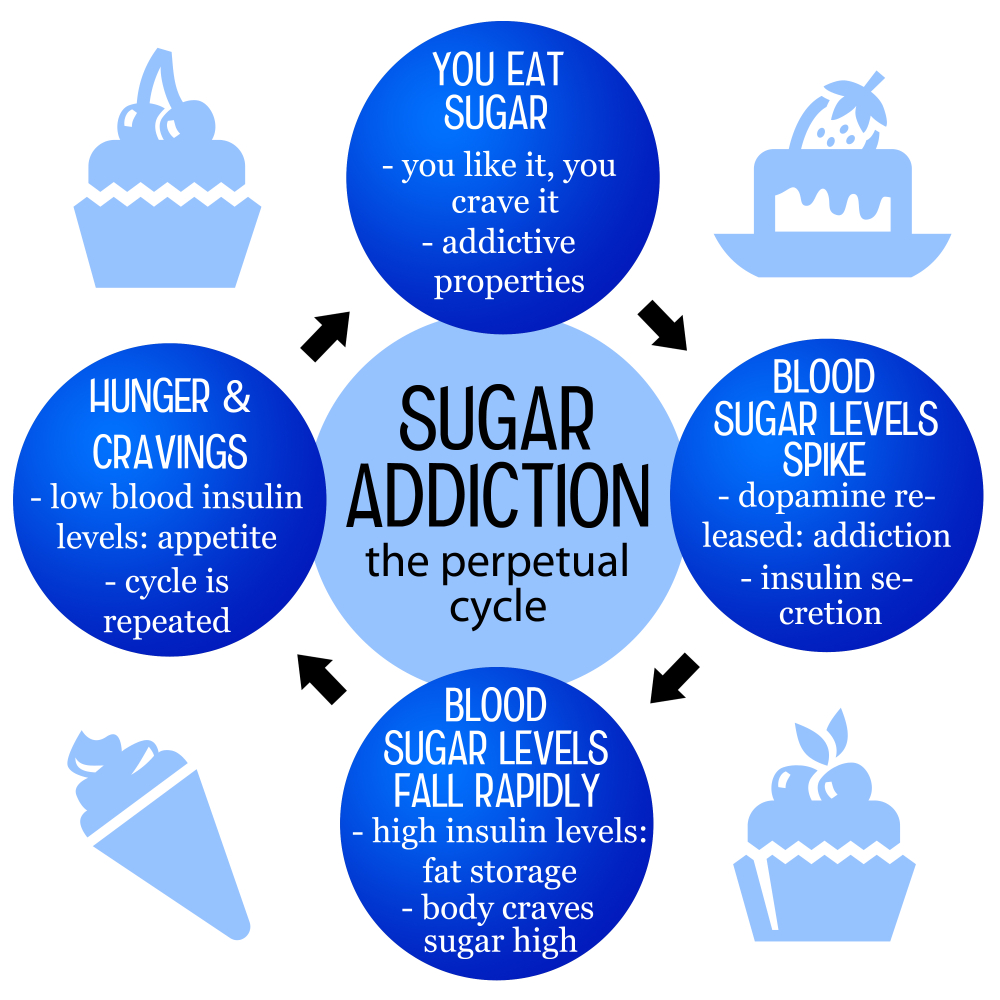
Sugar cravings are a common phenomenon, and many people experience them on a daily basis. This overwhelming desire for sweet foods can often lead to compulsive eating patterns, making it challenging to maintain a healthy diet. The impact of sugar on our brain chemistry, including dopamine release, plays a significant role in the development of these cravings. It’s important to recognize that while experiencing cravings is normal, the sheer volume of added sugar in our diets today can exacerbate these desires, leading to a cycle of sugar consumption that is hard to break.
Moreover, the modern food landscape is saturated with ultra-processed foods that are laden with added sugars, making it even more difficult for individuals to resist the temptation to indulge. These products are designed to be hyper-palatable, further intensifying cravings. To combat the effects of sugar cravings, it’s advisable to focus on whole foods that naturally contain sugar, such as fruits and vegetables, which provide essential nutrients without the negative side effects associated with added sugars.
The Debate: Is Sugar Addictive?
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked a significant debate in the health community. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive, sugar does not fit neatly into this category according to current clinical guidelines. Nevertheless, research indicates that sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive behavior reminiscent of other addictive substances. This is largely due to its ability to stimulate the brain’s reward system, leading to repeated consumption and making it difficult for some individuals to limit their intake.
This complexity is heightened by the fact that many people experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they reduce their sugar consumption, such as headaches, anxiety, and mood swings. These symptoms can mirror those associated with conventional addictive substances. Therefore, while sugar might not meet the strict criteria of addiction, its effects on the body and mind suggest that it does share some characteristics with addictive behaviors, raising the question of how society should approach added sugar consumption.
Health Effects of Excessive Sugar Consumption
The health effects of excessive sugar consumption are well-documented and significant. Consuming high amounts of added sugar can lead to a variety of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. In fact, the American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to reduce these risks, suggesting no more than 6-9 teaspoons per day depending on age and gender. Yet studies show that the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons daily, highlighting a critical public health concern.
Additionally, high sugar intake is associated with metabolic dysfunction and increases the likelihood of developing serious health conditions. The effects are seen not just physically but also psychologically, as excessive sugar can impact mood and energy levels. Therefore, being mindful of sugar consumption is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing chronic diseases. It’s vital to encourage people to read food labels and become aware of hidden sugars in their diets.
Strategies to Manage Sugar Addiction
Managing sugar consumption can be a challenging task, especially in a world where sugary snacks and beverages are readily available. A gradual reduction approach is recommended, allowing individuals to decrease their sugar intake without experiencing severe withdrawal symptoms. This might involve swapping sugary snacks for healthier alternatives, such as fruits or nuts, that fulfill cravings while providing nutritional benefits without excess added sugar.
Another effective strategy is to cultivate awareness about one’s eating habits. Keeping a food diary can help people identify patterns in their sugar consumption and understand the triggers behind their cravings. By focusing on whole, minimally processed foods and being mindful of portion sizes, individuals can create a balanced diet that satisfies their cravings while addressing the negative consequences of excessive sugar intake.
The Difference Between Natural and Added Sugars
Understanding the distinction between natural and added sugars is vital for making informed dietary choices. Natural sugars, found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, come with a wealth of nutrients and offer health benefits when consumed in moderation. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them an ideal choice for a healthy diet. In contrast, added sugars are present in many processed foods and beverages, contributing to caloric intake without offering significant nutritional value.
Added sugars can lead to health complications if consumed excessively, particularly when they contribute to the body’s total caloric intake without providing the necessary nutrients for health. Hence, while it’s important to enjoy sweets in moderation, prioritizing natural sugars and reducing added sugar intake can lead to better health outcomes and decrease the risk of sugar-related health issues.
How Sugar Impacts Our Mood and Energy Levels
Sugar consumption can have a profound effect on mood and energy levels. The immediate satisfaction derived from sugary foods can lead to a temporary boost in energy, followed by a crash that often leaves individuals feeling fatigued and irritable. This cycle can create a dependency on sugar for quick energy, contributing to unhealthy eating habits and emotional eating patterns.
In addition, the fluctuations in blood sugar levels due to high sugar consumption may lead to mood swings and increased anxiety. Studies have shown that individuals who consume high amounts of sugar may experience heightened symptoms of depression and anxiety. Therefore, finding a balance in sugar consumption is crucial for emotional well-being, as it not only affects physical health but also contributes to overall mood stability.
Curbing Sugar Cravings: Practical Tips
Curbing sugar cravings requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply saying no to sweets. Incorporating regular meals that include a balance of macronutrients – proteins, fats, and carbohydrates – can help regulate blood sugar levels and minimize cravings. Eating a variety of whole foods can also provide satisfaction and help avoid the slippery slope of turning to sugary snacks for comfort.
Moreover, staying hydrated is essential. Often, feelings of hunger can actually be signs of dehydration. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help curb cravings for sugary drinks and foods, enabling individuals to feel fuller and more energized. Keeping healthy snacks on hand can also make it easier to resist the temptation of sugary options.
The Role of Education in Reducing Sugar Consumption
Education plays a crucial role in reducing sugar consumption and promoting healthier eating habits. Understanding the health implications associated with high added sugar intake can motivate individuals to make better choices. Schools, communities, and health organizations can facilitate workshops and informational sessions to raise awareness about the hidden sugars found in everyday foods and beverages.
Furthermore, educational efforts should focus on practical strategies for making healthier food choices, such as reading nutrition labels and selecting whole foods. By equipping individuals with knowledge and skills to navigate the often-overwhelming landscape of dietary choices, we can empower them to reduce their added sugar consumption and improve their overall health.
The Impact of Social Influences on Sugar Consumption
Social influences significantly affect eating behaviors, including sugar consumption. Peer pressure, societal norms, and advertising can all play a role in the foods we choose. In environments where sugary snacks are prevalent, individuals may feel compelled to consume these items to fit in or seek social acceptance. Understanding the social dynamics that contribute to high sugar consumption can help individuals make more conscious choices.
Moreover, cultural attitudes towards food often shape our perceptions of sugar and its role in celebration and reward. Acknowledging these influences is essential in creating strategies to address excessive sugar consumption. Building supportive communities and encouraging healthier collective eating habits can help shift the narrative around sugar and foster healthier choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs or alcohol?
While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like drugs or alcohol. Research indicates that sugar may stimulate the brain’s reward system similarly, but the withdrawal symptoms are generally less severe.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to negative health effects, including weight gain, insulin resistance, and increased risk of chronic diseases. Consuming too much added sugar can contribute to unhealthy cravings and compulsive eating habits.
How do sugar cravings develop?
Sugar cravings often develop due to the consumption of ultra-processed foods high in added sugars. These foods are designed to be highly palatable, which can lead to habitual consumption and increase cravings for sweets.
Can you experience withdrawal symptoms from stopping sugar consumption?
Yes, some people may experience withdrawal-like symptoms, such as headaches, dizziness, or anxiety, when they reduce or eliminate added sugar from their diets. These symptoms are typically mild compared to those associated with addictive substances.
What is considered a healthy amount of added sugar consumption?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar consumption to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 teaspoons for women. Monitoring sugar intake can help reduce cravings and improve overall health.
What are some strategies to manage sugar cravings?
To manage sugar cravings, gradually reduce added sugar intake rather than quitting abruptly. Incorporate whole foods, like fruits and vegetables, into your diet, which naturally contain sugars along with essential nutrients.
Is sugar present in essential foods?
Yes, sugar is naturally present in various essential foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and dairy products. It’s important to distinguish between these natural sugars and the added sugars found in many processed foods.
Are there any long-term health effects of high added sugar consumption?
Long-term high added sugar consumption can lead to obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic health issues. It’s essential to be mindful of added sugar intake to maintain overall health.
How can I reduce my cravings for added sugar?
To reduce cravings, focus on a balanced diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, and fiber, which can stabilize blood sugar levels. Additionally, reading food labels and slowly decreasing sugar intake can help control cravings for sweets.
Why is it difficult to compare sugar to addictive substances?
It’s challenging to classify sugar alongside addictive substances like nicotine and alcohol because sugar is a necessary nutrient that can enhance flavor and enjoyment in moderation, whereas addictive substances can be entirely eliminated from one’s diet.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar and Addiction | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, despite cravings and compulsive behaviors. |
| Physical Effects | Withdrawal-like symptoms may occur when consumption stops, but they are less severe compared to other addictive substances. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | Foods high in added sugar, fat, and sodium are prevalent and increase cravings due to their palatability. |
| Sugar Consumption Recommendations | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Moderation is Key | While sugar has enjoyable qualities, excessive intake can lead to health issues. |
| Gradual Reduction | A sudden stop in sugar intake can backfire; gradual reduction is advised. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked significant debate among nutrition experts, with contrasting views and research presenting different aspects. While sugar does exhibit some addictive qualities by stimulating cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it fundamentally differs from substances like alcohol or nicotine as it is not classified as an addictive substance. Understanding the effects of sugar and managing intake is essential, especially given how prevalent it is in ultra-processed foods. The key lies in moderation and awareness to promote health without sacrificing the sweetness that can be a delightful part of our diets.