Stem cell therapy for corneal damage is emerging as a groundbreaking solution in the field of eye care. This innovative approach has demonstrated a remarkable ability to restore corneal surface integrity in patients with severe eye injuries, particularly those caused by limbal stem cell deficiency. By harnessing the power of cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), surgeons can now provide unprecedented relief from the debilitating symptoms associated with corneal damage, such as persisting pain and vision loss. Recent clinical trials have shown that this procedure is not only safe but also achieves exceptional success rates, making it a promising option for those previously deemed untreatable. Moreover, with advancements in corneal surface restoration techniques, the potential for broader applications in eye damage treatment is becoming a reality.
The field of ocular regenerative medicine is witnessing a significant transformation, especially with the advent of therapies targeting corneal injuries. Alternative methods involving harvested limbal stem cells present a novel avenue for patients suffering from chronic visual impairments due to corneal surface disorders. Techniques such as CALEC surgery are garnering attention for their safety and efficacy in not only repairing damaged ocular surfaces but also enhancing overall visual outcomes. As researchers continue to explore clinical trial stem cells and their applications, the prospect of a new standard in eye care is on the horizon. This revolutionary approach to limbal stem cell transplantation is redefining how we understand and treat ocular damage.
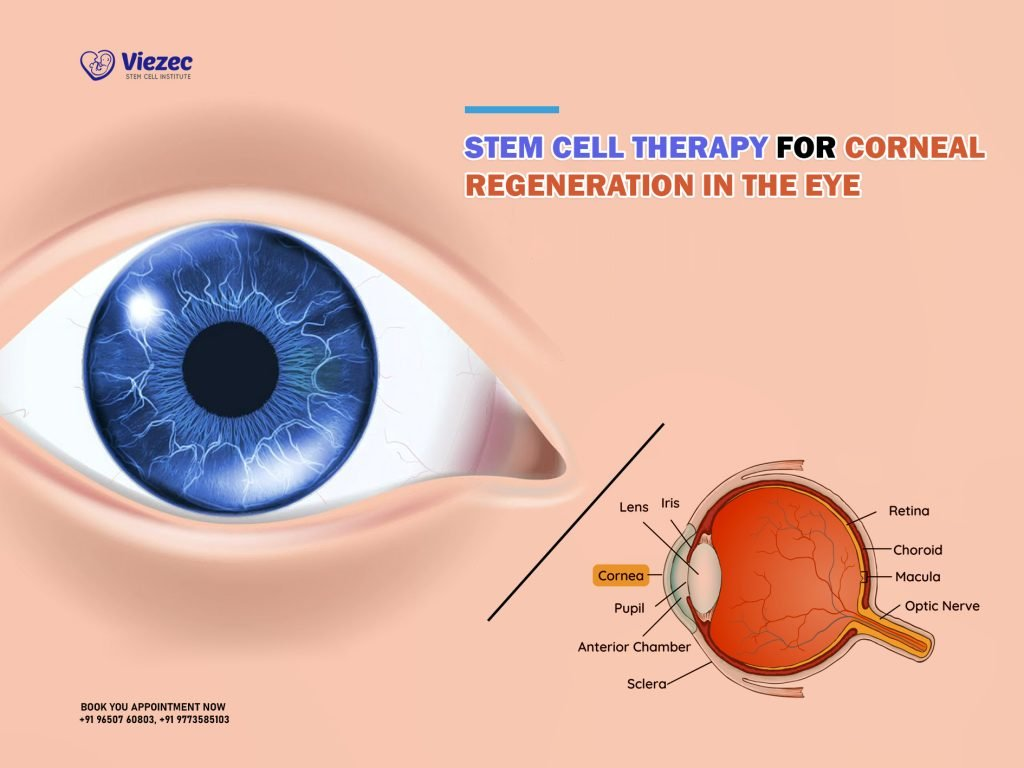
Understanding Corneal Surface Restoration
Corneal surface restoration plays a crucial role in the treatment of eye injuries and diseases that compromise visual acuity. The corneal surface, primarily composed of limbal epithelial cells, is vital for maintaining transparency and overall eye health. When these cells are depleted due to trauma, infection, or other factors, the eye can suffer from severe complications, including pain and irreversible vision loss. Restoration procedures aim to replenish these cells and restore the corneal surface, leading to improved vision and quality of life for patients.
One of the most promising advancements in corneal surface restoration is the development of stem cell therapies, specifically cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC). CALEC therapy utilizes the patient’s own healthy stem cells to regenerate the damaged cornea, showcasing high effectiveness and safety in clinical trials. By capitalizing on regenerative medicine principles, this therapy offers new hope to individuals suffering from conditions once deemed untreatable.
The Role of CALEC Surgery in Eye Damage Treatment
CALEC surgery has emerged as a groundbreaking approach in the field of eye damage treatment, particularly for individuals with corneal injuries resulting from limbal stem cell deficiency. This innovative procedure involves harvesting limbal stem cells from a healthy eye, then culturing these cells to create a graft that can be transplanted into the damaged eye. The safety and effectiveness demonstrated in clinical trials have positioned CALEC as a pivotal option for restoring vision and alleviating discomfort for many patients.
This surgical intervention marks a significant advancement in regenerative medicine, providing a viable alternative to traditional corneal transplant procedures. With success rates showing over 90% in restoring corneal surfaces, CALEC surgery is transforming how we manage severe eye injuries. The ability to use a patient’s own cells for the procedure reduces the risks of rejection and additional complications, significantly enhancing the overall treatment experience.
Exploring Limbal Stem Cells and Their Potential
Limbal stem cells are a vital component of the ocular surface, essential for the continuous renewal and repair of the corneal epithelium. These cells are located at the limbus, the border between the cornea and the sclera, and are responsible for maintaining corneal integrity. When injuries occur, such as chemical burns or infections, the depletion of these cells can lead to limbal stem cell deficiency and lasting corneal damage, necessitating advanced treatments like CALEC.
Recent research highlights the importance of limbal stem cells not only for their regenerative capabilities but also for their role in cutting-edge stem cell therapies. By isolating and expanding these cells, researchers can create grafts that significantly improve patient outcomes. The exploration of limbal stem cells continues to fuel innovations that will potentially change the landscape of eye care, especially for patients suffering from previously untreatable conditions.
Advancements in Clinical Trials for Stem Cells
Clinical trials represent a critical phase in determining the safety and efficacy of new treatments, particularly in the realm of stem cell therapy for eye damage. The recent clinical trial of CALEC has provided substantial evidence supporting its effectiveness in restoring the corneal surface of patients with limbal stem cell deficiency. Following a structured protocol involving rigorous preclinical studies, the trial has shown encouraging results, establishing a solid foundation for future research and potential FDA approval.
Moreover, the trial’s success at Mass Eye and Ear indicates a growing trend towards incorporating stem cell therapies into mainstream eye care. With participation from various research institutions, these clinical trials not only enhance our understanding of treatment protocols but also pave the way for innovative practices in ocular medicine, ultimately benefiting a broader patient demographic.
Evaluating the Safety Profile of CALEC Treatment
Safety is a paramount consideration in any medical treatment, especially when involving human participation in clinical trials. The CALEC trial indicated a robust safety profile, with no severe complications reported among participants. The occurrence of minor adverse events, such as bacterial infections, illustrates the importance of continued monitoring and care in post-transplantation settings. The findings underscore that with proper protocols and patient selection, stem cell therapies can be both effective and safe.
The commitment to patient safety, combined with effective outcomes, fosters greater confidence among both patients and healthcare providers regarding CALEC procedures. As research in this field continues to evolve, ongoing assessments of safety and efficacy will remain essential for refining therapeutic techniques and enhancing patient care across ophthalmology.
Limitations and Future Directions of Stem Cell Therapy
While the CALEC procedure has shown significant promise, limitations still exist, particularly regarding patient eligibility. As this procedure requires the extraction of stem cells from a healthy eye for transplantation into a damaged eye, it is currently not suitable for patients with bilateral ocular damage. Future research is focused on developing allogeneic approaches using donor limbal stem cells, which could widen eligibility and increase the number of treated individuals.
Additionally, comprehensive studies involving larger and more diverse patient cohorts are essential for understanding the long-term impacts and potential challenges of CALEC surgery. By advancing research methodologies and designs, including randomized control trials, the field can better evaluate the potential for widespread implementation of this innovative therapy.
The Role of FDA Approval in Stem Cell Treatments
The pathway to FDA approval is crucial for any new medical treatment, including stem cell therapies like CALEC. This regulatory process ensures that treatments meet established safety and efficacy standards before becoming widely available to the public. The successful completion of the CALEC trial signifies a critical step towards achieving this goal, demonstrating that rigorous clinical evaluation can bring forth revolutionary therapies in eye care.
Achieving FDA approval not only earmarks a treatment as safe and effective but also facilitates broader access to innovative therapies for patients across the nation. Collaboration between researchers, regulatory bodies, and healthcare institutions can expedite the translation of scientific findings into clinical practices, ultimately resulting in improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
Patient Outcomes and Vision Improvement with CALEC
One of the most compelling aspects of the CALEC clinical trial is the positive impact on patient outcomes, particularly regarding vision quality and overall satisfaction. Participants have reported varying degrees of improvement in visual acuity following graft transplantation, demonstrating the procedure’s effectiveness in restoring not just corneal health but also functional vision. With ongoing follow-ups confirming sustained results, CALEC therapy is changing the narrative on treatable corneal injuries.
Moreover, the psychological and emotional benefits derived from improved vision cannot be overstated. Patients who previously faced potential blindness due to severe corneal damage now have renewed hope for regaining everyday functionality and a better quality of life. This paradigm shift in treatment capabilities underscores the need for continued investment and research in stem cell therapies for eye damage.
Collaboration: The Key to Advancing Eye Health Research
The progress seen in CALEC therapy and similar treatments owes much to collaborative efforts among research institutions, clinical teams, and funding bodies. Strategic partnerships among diverse scientific and medical communities facilitate knowledge exchange, innovative ideas, and clinical best practices. Institutions like Mass Eye and Ear and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute illustrate how teamwork can drive advances in treatment and support clinical translation of cutting-edge research into reapable therapies for patients.
Moving forward, fostering collaboration will be vital in addressing the complex challenges posed by corneal diseases. By leveraging collective expertise, sharing resources, and maintaining open communication channels, researchers can unlock new possibilities and refine existing methodologies, ensuring that effective treatments like CALEC reach individuals who need them most.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is stem cell therapy for corneal damage and how does it work?
Stem cell therapy for corneal damage involves using cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) extracted from a healthy eye to restore the surface of a damaged cornea. A biopsy is performed on the healthy eye to obtain limbal stem cells, which are then expanded into a cellular tissue graft and transplanted into the affected eye. This innovative approach aims to treat corneal injuries that conventional methods cannot address.
What is CALEC surgery and who developed it?
CALEC surgery, or cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell surgery, is a procedure developed at Mass Eye and Ear to treat corneal damage. It utilizes limbal stem cells harvested from a healthy eye to regenerate the corneal surface in patients with significant injuries or diseases affecting vision. It represents a significant advancement in eye damage treatment.
What is the success rate of stem cell therapy for corneal damage based on recent clinical trials?
Recent clinical trials have shown that stem cell therapy for corneal damage using CALEC has a high success rate, with over 90% effectiveness in restoring the corneal surface. After 18 months of follow-up, results indicated a complete success rate of 77% with various degrees of visual improvement in patients.
What conditions can stem cell therapy for corneal damage treat?
Stem cell therapy for corneal damage is effective for conditions that lead to limbal stem cell deficiency, such as chemical burns, infections, and traumatic injuries to the eye that deplete the limbal epithelial cells. This therapy provides hope for patients with corneal damage who previously had limited treatment options.
What are limbal stem cells and why are they important in corneal surface restoration?
Limbal stem cells, located at the outer border of the cornea, are crucial for maintaining a healthy corneal surface. They regenerate the epithelial layer, ensuring clarity and proper function of the eye. In cases of injury, these stem cells can become depleted, leading to vision impairment and persistent pain, making their restoration through stem cell therapy essential for effective eye damage treatment.
Is stem cell therapy for corneal damage currently available to patients?
As of now, stem cell therapy for corneal damage, specifically CALEC surgery, remains experimental and is not yet widely available in hospitals. Further research and clinical trials are necessary to establish its efficacy and safety before submitting for federal approval.
What are the potential future advancements in stem cell therapy for corneal damage?
Future advancements in stem cell therapy for corneal damage may include the development of an allogeneic manufacturing process using limbal stem cells from donor eyes. This could expand the treatments available for patients suffering from corneal damage in both eyes, enhancing accessibility and effectiveness.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Stem Cell Therapy Overview: CALEC (Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cells) involves harvesting stem cells from a healthy eye to transplant into a damaged eye. |
| Clinical Trial Results: 14 patients treated over 18 months demonstrated over 90% effectiveness in restoring corneal surfaces, with complete restoration in 50% at 3 months, rising to 79% at 12 months and 77% at 18 months. |
| Safety Profile: No severe incidents reported in donor or recipient eyes; one minor infection related to chronic contact lens use was noted. |
| Future Directions: Researchers aim to develop an allogeneic process for patients with damage to both eyes, which could broaden treatment accessibility. |
| Trial Limitations: The procedure is experimental and currently not available for general use; further studies are needed for FDA approval. |
| Funding and Support: The study is funded by the National Eye Institute and represents significant advancement in stem cell therapy for the eye in the U.S. |
Summary
Stem cell therapy for corneal damage presents a revolutionary solution for individuals suffering from previously untreatable eye injuries. The successful clinical trial conducted at Mass Eye and Ear showcases the potential of CALEC treatment in restoring corneal surfaces, offering hope for enhanced vision and quality of life. As research progresses, the possibility of broader applications for treating more severe cases of corneal damage is becoming increasingly feasible, marking a significant milestone in ocular medicine and regenerative therapy.