Suicide prevention for older adults is a pressing issue that demands immediate attention, particularly given the alarming statistics indicating that individuals aged 75 and older face the highest suicide rates of any age group. Despite their vulnerability, older adults have access to few mental health resources tailored specifically for them, highlighting a significant gap in support for elderly individuals. Recent research from the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry illustrates how prevalent online resources often overlook the unique needs of this demographic. With an increase in social isolation and mental health struggles among seniors, there is an urgent call for targeted elderly suicide prevention strategies. By addressing these challenges and enhancing the accessibility of mental health resources for seniors, we can potentially save lives and create a supportive framework for older adults in crisis.
Addressing the challenges associated with the well-being of seniors is crucial, especially as their mental health often goes unrecognized. The increasing rates of self-harm in this demographic underscore the need for effective measures focused on late-life mental health crises. Resources must be developed and made readily available to support aging individuals grappling with suicidal thoughts, as they frequently experience feelings of isolation and despair. Suicide prevention tailored specifically for this population can empower seniors and encourage them to seek help. It is imperative that both healthcare providers and society at large recognize and respond to the emotional needs of older adults to ensure their safety and well-being.
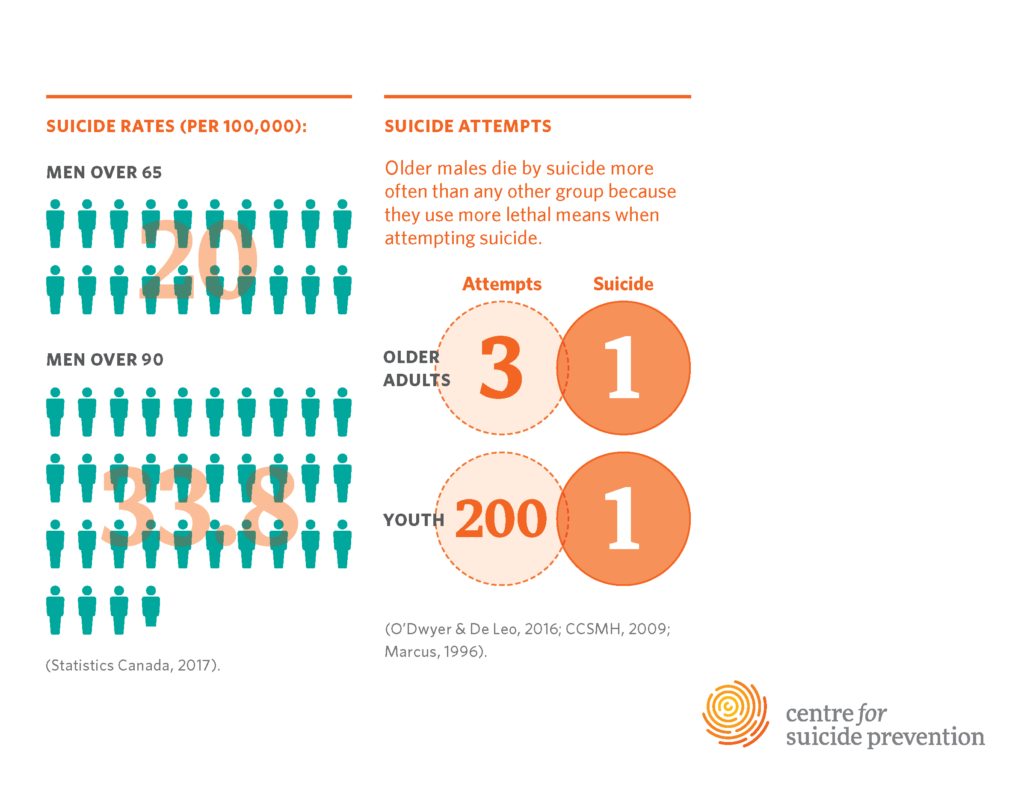
Understanding the Risks: Suicide Rates in Older Adults
Older adults face unique challenges that significantly contribute to their elevated suicide rates, particularly in those aged 75 and older. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this demographic experiences a staggering suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000. Factors such as social isolation, chronic health conditions, and the emotional burden of loss and grief can exacerbate these risks, leading to feelings of hopelessness and despair among seniors. Additionally, the stigma surrounding mental health can prevent older adults from seeking help, leaving them vulnerable at a critical time in their lives.
Recognizing the scope of this issue is vital for effective interventions. Research indicates that many older adults may not be aware of the level of support available, or worse, they may encounter barriers when searching for mental health resources. As health organizations and advocates become aware of these alarming statistics, they must work collaboratively to ensure that suicide prevention efforts include clear and accessible information tailored specifically for the elderly. This could involve establishing comprehensive outreach programs that address the unique psychosocial factors facing older individuals.
The Need for Targeted Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
The findings from the recent study highlight a critical gap in the availability of suicide prevention resources aimed specifically at older adults. Despite their high susceptibility to suicide, these individuals often find themselves unrepresented in national campaigns and programs. In response, it’s essential to develop and implement targeted interventions that resonate with the elderly population. These initiatives should not only inform older adults about available resources but also encourage them to actively engage with mental health services.
Tailoring suicide prevention efforts for the elderly requires careful consideration of their unique needs. For instance, creating informative materials that are easy to read and understand can help older adults feel more comfortable accessing these resources. Moreover, providing direct support through community programs, helplines, and workshops can foster an environment where older individuals feel valued and heard. By prioritizing suicide prevention for older adults, society can begin to address the disparities that have long affected this vulnerable population.
Enhancing Mental Health Resources for Seniors
As the demand for mental health services among older adults continues to rise, it is imperative to enhance the existing resources available to this population. Many elders may not be aware of the mental health resources specifically designed for them, which could prove vital in times of crisis. These resources can include dedicated hotlines, therapists specializing in geriatric psychiatry, and community support groups that provide a sense of belonging and understanding. By promoting these mental health resources, we can empower seniors to take charge of their mental well-being.
Furthermore, mental health professionals need to focus on developing strategies for outreach and education that resonate with older adults. For example, incorporating technology into therapy, such as telehealth sessions, can bridge the gap for seniors who may have mobility issues or transportation challenges. By expanding access to mental health resources through various channels, older adults can find the help they need without the fear of stigma or embarrassment.
The Role of Geriatric Psychiatry in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in addressing the mental health needs of older adults, particularly concerning suicide prevention. Specialists in this field understand the complexities of aging and mental health, offering tailored approaches that can effectively target the root causes of suicidal ideation among seniors. By focusing on comprehensive mental health evaluations and personalized care plans, geriatric psychiatrists can provide older individuals with the support and resources they need to navigate their emotional challenges.
Additionally, geriatric psychiatry emphasizes the importance of collaboration among healthcare providers to ensure a holistic approach to senior mental health. This could mean integrating mental health care with primary healthcare services to create a seamless experience for the elderly. As families often play a vital role in supporting their loved ones, educating caregivers about the signs of depression and suicide risk can enhance this multidisciplinary approach, fostering a therapeutic environment where older adults feel safe and supported.
Building Support Systems for Elderly Suicide Prevention
Creating robust support systems is essential for the successful prevention of suicide among older adults. Engaging community organizations and non-profits to form networks of support can provide seniors with a safety net that enhances their mental health resilience. These support systems should offer a variety of programs, from social gatherings to counseling services, allowing older individuals to connect with peers and form meaningful relationships. By fostering a sense of community, we can help combat feelings of isolation that often lead to suicidal thoughts.
Moreover, community-based initiatives that aim to educate not only the elderly but also their families about suicide prevention are critical. Workshops and seminars can empower seniors with knowledge and resources, while also providing families with the tools to identify warning signs of mental health crises. By equipping families with this information, we can create a more nurturing environment that prioritizes open conversations about mental health and encourages older adults to seek help when needed.
Online Resources: Navigating Mental Health for Seniors
In today’s digital world, online resources represent a powerful avenue for older adults seeking mental health support. However, as highlighted in the recent study, many older individuals struggle to navigate these resources effectively. There is a pressing need for user-friendly websites and platforms that cater specifically to seniors, ensuring that information about mental health, suicide prevention, and supportive services is readily accessible. Simplifying the search process can dramatically increase the likelihood that older adults will utilize available resources.
Additionally, leveraging technology to deliver mental health resources directly to older adults can bridge the gap in access to care. For instance, online support groups and mental health forums tailored for seniors can provide a safe space for them to share their experiences and feelings. Educating older adults on how to utilize these platforms, coupled with encouragement from healthcare professionals, can empower them to address their mental health needs proactively.
Addressing Social Isolation Among Seniors
Social isolation has emerged as a key factor in elevated suicide rates among older adults, making it imperative to tackle this issue head-on. Many seniors live alone and may experience dwindling social networks as friends and family pass away. This loneliness can contribute to feelings of despair and may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts. Community initiatives focused on promoting inclusivity and connection can be a game-changer, providing seniors with opportunities to engage with others and build new relationships.
Support groups, local clubs, and volunteer opportunities can help alleviate feelings of isolation by encouraging older adults to interact with their peers. Programs that offer transportation or virtual meeting options can further enhance participation and foster connections over shared interests. By prioritizing social engagement, communities can create environments where older adults feel valued and supported, which is critical in suicide prevention efforts.
The Importance of Research on Geriatric Mental Health
Research is essential in advancing our understanding of geriatric mental health, particularly in the realm of suicide prevention. As highlighted in the study from McLean Hospital, there remains a significant gap in our knowledge regarding effective interventions for older adults facing suicidal thoughts. By investing in research that focuses on the mental health of this population, we can uncover new insights and develop tailored strategies that address their unique needs.
Moreover, ongoing studies contribute to the visibility of elderly mental health issues, prompting policymakers and healthcare organizations to allocate more resources toward this critical area. Increased funding for research can lead to innovative programs and campaigns designed specifically for older adults, ultimately improving their access to necessary mental health resources. The collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and community organizations is vital in creating a comprehensive framework for effective elderly suicide prevention.
Conclusions and Future Directions for Elderly Suicide Prevention
As we reflect on the pressing issue of suicide among older adults, it is clear that significant changes are needed to enhance prevention efforts. Strategies must evolve to address the unique challenges faced by seniors, including social isolation, mental health stigma, and lack of access to appropriate resources. For the future of elderly suicide prevention, it is essential to foster an informed community that acknowledges this issue and actively works together to provide targeted support.
The next steps should include advocating for policy changes that prioritize mental health resources for older adults, alongside the development of community-driven initiatives that focus on prevention education. By combining efforts on multiple fronts, including research, community support, and healthcare practices, we can create a robust framework that prioritizes the mental health and well-being of our elderly population. Ensuring that no older adult feels alone in their struggles is not just a goal but a necessity in preventing needless tragedies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key resources available for suicide prevention for older adults?
Suicide prevention for older adults includes a variety of resources such as hotlines, community support groups, and mental health services specifically designed for seniors. Organizations focused on elderly suicide prevention often provide tailored information, and local Area Agencies on Aging can also connect seniors to mental health resources for seniors.
How can families contribute to suicide prevention for older adults?
Families play a crucial role in suicide prevention for older adults by staying connected, recognizing signs of depression or social withdrawal, and encouraging open conversations about mental health. Additionally, educating themselves about the resources available for elderly suicide prevention can empower families to provide appropriate support for their loved ones.
What are the warning signs of suicidal thoughts in older adults?
Warning signs of suicidal thoughts in older adults may include noticeable changes in mood, withdrawal from social activities, feelings of hopelessness, or expressings thoughts of wanting to die. Awareness of such signs is vital for effective suicide prevention for older adults.
What is the impact of mental health resources for seniors on suicide rates in older adults?
Access to mental health resources for seniors can significantly lower suicide rates in older adults by providing crucial support and intervention. Improved access to geriatric psychiatry services and community mental health initiatives specifically targeting elders can aid in their overall mental well-being and reduce feelings of isolation.
Why are suicide rates in older adults increasing despite existing prevention efforts?
Suicide rates in older adults are increasing due to factors such as social isolation, unmet mental health needs, and underrepresentation in research that shapes prevention efforts. Enhanced focus on tailored suicide prevention for older adults and adequate funding for targeted initiatives is urgently needed.
What role does social isolation play in elderly suicide prevention?
Social isolation is a significant risk factor for elderly suicide, leading to increased feelings of loneliness and depression. Effective suicide prevention for older adults requires strategies to reduce isolation, such as community engagement and promoting connections with friends and family.
How can community programs support suicide prevention for older adults?
Community programs can greatly enhance suicide prevention for older adults by providing social activities, mental health workshops, and regular outreach efforts to check on seniors. These initiatives create supportive environments where elderly individuals can feel valued and connected.
What strategies can improve access to mental health resources for seniors?
Improving access to mental health resources for seniors involves increasing awareness of available services, simplifying access through online platforms, and promoting mobile outreach programs that cater to the unique healthcare needs of older adults.
What should be included in effective suicide prevention campaigns targeting older adults?
Effective suicide prevention campaigns targeting older adults should include accessible mental health resources for seniors, tailored messaging that resonates with their experiences, and platforms that reach seniors where they are, such as community centers and healthcare facilities.
How can healthcare providers enhance support for elderly suicide prevention?
Healthcare providers can enhance support for elderly suicide prevention by regularly screening older patients for mental health issues, fostering open communication about suicidal thoughts, and referring them to specialized geriatric psychiatry services and community resources.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Older Adults at Risk | Adults aged 75 and older have the highest rates of suicide of any age group. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations lack accessible resources targeting older adults. |
| Study Insights | Research indicates an imbalance in online suicide prevention efforts targeting younger populations over older adults. |
| Social Isolation and Loneliness | Increased suicide rates among older adults may be linked to social isolation and loneliness. |
| Call for Action | There is an urgent need for tailored campaigns and resources for suicide prevention aimed at older adults. |
| Research Support | The study was funded by various institutions, emphasizing the need for more research in the field. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is critical, as this age group faces the highest risk of suicide, particularly those aged 75 and older. The recent study highlights a significant gap in the available resources for this demographic, who often encounter barriers when seeking help online. Addressing the unique healthcare needs of older adults through targeted prevention efforts is essential in mitigating the rising suicide rates in this population. Increased awareness and funding for tailored campaigns can help bridge the resource gap and support the mental health of older adults.