Bile Imbalance Linked to Liver Cancer: Key Findings
- admin
- 0
- Posted on
Bile imbalance liver cancer has emerged as a critical area of study, especially as researchers uncover the links between bile acid regulation and liver health. This newly highlighted relationship indicates that disruptions in bile acid metabolism can lead to serious liver conditions, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent investigations have identified a key molecular switch that plays a pivotal role in this imbalance, presenting novel avenues for liver cancer treatment. As scientists delve deeper into the YAP FXR relationship, the implications for both understanding and combating liver diseases become clearer. The findings, which emphasize the role of bile acids as more than mere digestive agents, pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies that target the underlying mechanisms of liver cancer progression.
Investigating bile acid dysregulation as it relates to hepatic malignancies is vital for improving health outcomes. This imbalance not only affects digestion but also contributes significantly to the development of disorders like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The interplay between bile acids and liver functions raises important questions about metabolic pathways and their implications for cancer treatment. Understanding the YAP and FXR relationship could lead to targeted therapies that effectively mitigate liver damage and cancer progression. As research in bile metabolism advances, it promises to unlock potential solutions in the fight against liver-related diseases.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and its Link to Liver Cancer
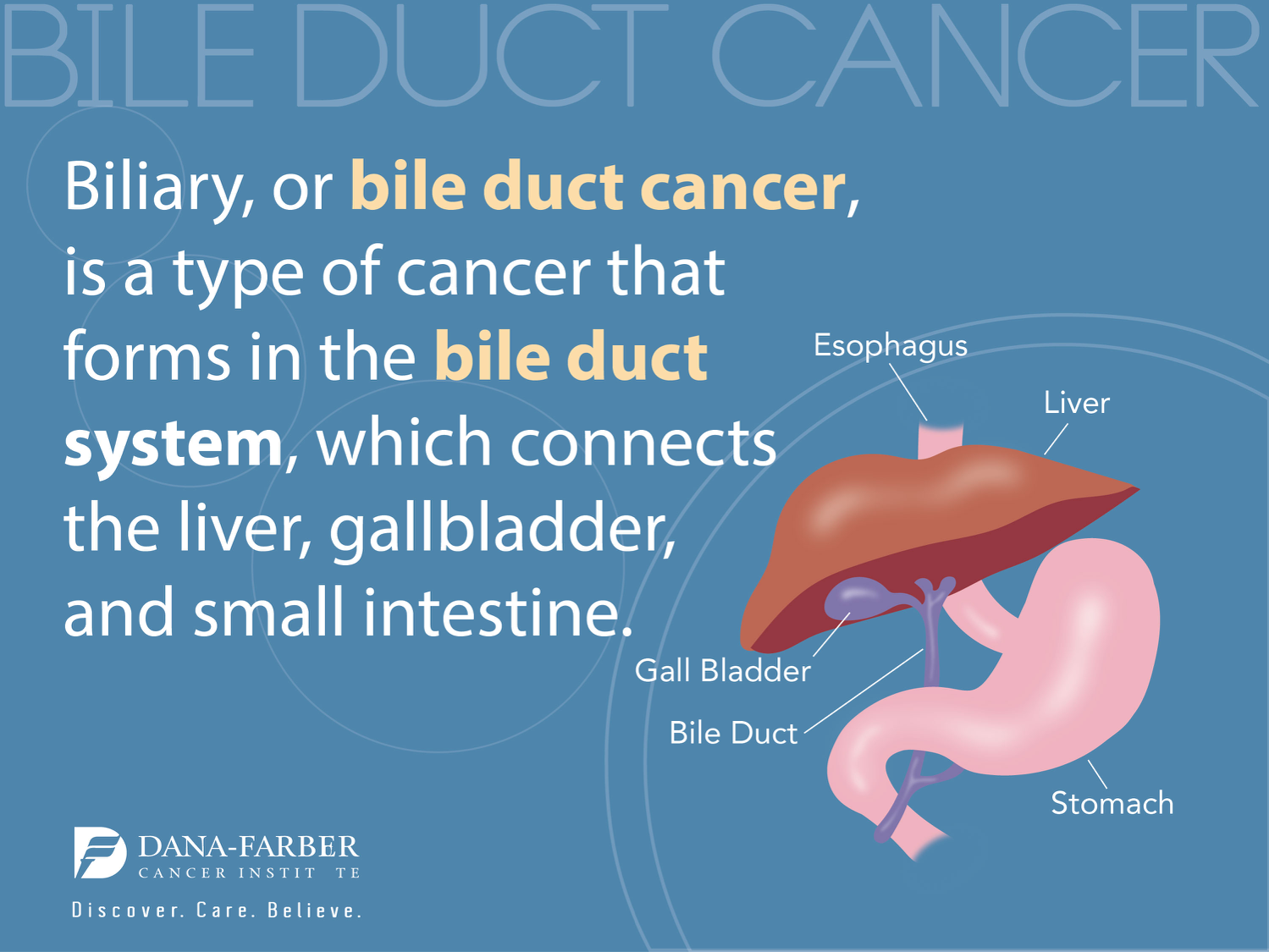
Bile imbalance plays a significant role in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver produces bile acids that are crucial for digesting fats, but when the balance of these bile acids is disrupted, it can lead to serious health complications, including liver cancer. Recent studies indicate that an overproduction of bile acids can accumulate in the liver, causing inflammation and fibrosis, which are precursors to cancer development. Addressing bile acid metabolism is essential in understanding the mechanisms behind liver diseases and formulating effective liver cancer treatment plans.
Understanding the interplay between bile acids and liver health extends into molecular biology, specifically within pathways like the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway. This pathway’s dysfunction results in an imbalance of bile acids that contributes to liver damage. Researchers are focusing on regulatory molecules like the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), which are pivotal in maintaining bile homeostasis. By manipulating this balance, it is possible to develop pharmacological treatments that can mitigate the accumulation of harmful bile acids, ultimately reducing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
The Role of YAP in Bile Acid Regulation
YAP (Yes-associated protein) has emerged as a critical component in the regulation of bile acid metabolism, which has significant implications for liver cancer treatment. Typically associated with promoting cell growth, YAP also functions as a repressor of FXR, a key nuclear receptor in bile acid homeostasis. When YAP inhibits FXR, it leads to the overproduction of bile acids, subsequently contributing to liver inflammation and an increased risk of HCC. Understanding this relationship highlights the complexity of cell signaling mechanisms involved in liver diseases.
Recent findings in the study of YAP suggest that rather than solely promoting cancerous growth, YAP’s repression of FXR can be targeted to manage bile metabolism and cancer progression. Researchers propose that disrupting YAP’s repressor function may bolster FXR activity, thus facilitating bile acid excretion and maintaining liver health. These insights open avenues for innovative liver cancer treatments aimed at modulating bile acid metabolism through the Hippo/YAP pathway.
Exploring Bile Acid Metabolism’s Impact on Liver Health
Bile acids are not just involved in fat digestion; they also play critical roles in metabolic regulation. Their production and metabolism are tightly controlled processes managed by various factors, including dietary intake and gut microbiota. Any imbalance in bile acid composition can lead to various liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. By investigating bile acid metabolism, researchers aim to uncover how these compounds influence liver health and disease progression. A deeper understanding of bile acid pathways can lead to the development of targeted treatments for liver diseases.
Furthermore, the relationship between bile acids and liver cancer emphasizes the importance of maintaining a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle to support liver function. Dietary changes that enhance bile acid metabolism could contribute to better liver health outcomes. This holistic approach, combined with targeted therapeutic advancements in the regulation of bile acids and their receptors, holds promise for addressing liver conditions and potentially reversing the trajectory toward liver cancer.
Pharmacological Advances in Liver Cancer Treatment
The exploration of how to manipulate bile acid metabolism opens new doors for pharmacological advancements in liver cancer treatment. By targeting FXR and its pathways, researchers are looking for ways to create drugs that enhance FXR function, potentially preventing the progression of liver disease. Such pharmacological solutions could alter the course of liver cancer treatment, offering hope for better patient outcomes. Current studies are examining the efficacy of certain compounds that can activate FXR, thus promoting proper bile acid regulation.
In addition, addressing the activity of proteins involved in bile acid export, such as BSEP, is critical for developing comprehensive treatment approaches. By enhancing bile acid excretion, it may be possible to alleviate the harmful effects of bile acid accumulation in the liver. These innovative strategies aim not only to halt the progression of liver cancer but also to create a more favorable environment for recovery and rehabilitation.
Cell Signaling Mechanisms in Liver Biology
The intricate cell signaling mechanisms that govern liver biology are pivotal to understanding how liver diseases develop and progress. The Hippo/YAP pathway, which plays a vital role in regulating cell growth and differentiation, has been identified as significantly influencing bile acid metabolism. Investigating how these pathways interact with liver function could reveal potential targets for liver cancer therapy. Understanding the molecular underpinnings of liver biology is essential for innovating new treatments and improving patient outcomes.
Moreover, research into these signaling pathways not only applies to liver cancer but also extends to other liver-related pathologies. By clarifying the roles of various molecular players in liver health, including the interactions between bile acids and regulatory proteins, researchers can develop holistic strategies for managing liver diseases. Continued exploration in this area will potentially translate to clinical advancements, providing effective interventions tailored to the complex nature of liver disorders.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Bile Acid Metabolism
Lifestyle choices play a critical role in influencing bile acid metabolism and, consequently, liver health. Diet, exercise, and overall wellness can affect how bile acids are produced and metabolized in the liver. Increased physical activity and a balanced diet rich in fiber can facilitate a more favorable bile acid composition, promoting liver health and potentially preventing diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding these lifestyle factors is essential for establishing preventive strategies in high-risk populations.
Additionally, body weight and obesity have been shown to impact bile acid profiles and liver function. Excess fat accumulation can lead to fatty liver diseases, increasing the risk of liver cancer. By promoting lifestyle interventions focusing on weight management and nutritional health, there is a potential to enhance bile acid metabolism, thereby supporting liver health. Public health initiatives targeting these lifestyle modifications could be instrumental in reducing the incidence of liver cancer on a larger scale.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Research
The future of liver cancer research lies in a multifaceted approach that integrates molecular biology, pharmacology, and lifestyle interventions to combat hepatocellular carcinoma. As ongoing studies unveil more about bile acid metabolism and the YAP-FXR relationship, researchers are hopeful for breakthroughs that can translate into novel therapeutics. Understanding how to manipulate these molecular pathways could lead to targeted therapies that significantly improve patient outcomes in liver cancer treatment.
Additionally, as research continues to explore the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to liver cancer risk, personalized medicine will play an increasingly important role in treatment strategies. Tailoring interventions based on individual metabolic profiles and lifestyle choices will allow for more effective management of liver health, paving the way for innovative approaches to tackling liver cancer.
The Interplay between Gut Microbiota and Bile Acids
The gut microbiota has a profound impact on bile acids and overall liver health. Emerging research indicates that gut bacteria can influence bile acid composition, metabolism, and signaling pathways that are linked to liver diseases. An imbalance in gut microbiota can disrupt bile acid homeostasis, potentially leading to liver inflammation and liver cancer. Understanding this intricate relationship may offer new avenues for therapeutic interventions aimed at promoting liver health.
Furthermore, strategies that include modifying the gut microbiome through dietary changes or probiotics may help restore balance to bile acid metabolism. This approach could enhance the body’s ability to manage bile acids more effectively, benefiting liver function. By investigating the gut-liver axis, researchers are exploring innovative ways to prevent and treat liver diseases through comprehensive management of both the microbiome and bile acid regulation.
Clinical Implications of Bile Acid Research
The findings from research into bile acids and their regulation have significant clinical implications for liver cancer treatment. Understanding the mechanisms that lead to bile acid imbalance provides critical insights into potential therapeutic targets. As researchers work to develop drugs that can enhance FXR activity or suppress YAP function, there is hope that novel treatments will emerge that can improve outcomes for patients diagnosed with liver cancer.
Moreover, integrating bile acid research into clinical practice may lead to more effective monitoring and management of liver health. For patients at high risk of liver cancer, targeted interventions that focus on bile acid metabolism could serve as preventive measures. As new technologies and pharmacological approaches are developed, the translation of these discoveries into real-world applications will be essential in combating liver diseases and improving public health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance can lead to liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When bile acids are overproduced due to disruptions in bile acid metabolism, it can result in liver inflammation and fibrosis, which are precursors to liver cancer.
How does bile acid metabolism relate to liver cancer treatment?
Understanding bile acid metabolism is crucial for liver cancer treatment. Research shows that targeting the FXR receptor, which regulates bile acid homeostasis, may offer new pharmacological solutions for preventing or treating liver cancer by alleviating bile acid buildup.
What role does the YAP FXR relationship play in liver cancer development?
The YAP FXR relationship is significant in liver cancer development. YAP, when activated, represses FXR function, disrupting bile acid metabolism and leading to liver damage, inflammation, and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma. Targeting this pathway could be key in developing therapeutic approaches.
What are bile acids and how do they affect liver health?
Bile acids are crucial for digesting fats and play a hormone-like role in metabolic processes. An imbalance in bile acids can cause liver injury, inflammation, and is linked to conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma, highlighting their significance in liver health.
Can enhancing FXR function be a potential strategy for liver cancer prevention?
Yes, enhancing FXR function may be a promising strategy for liver cancer prevention. By restoring proper bile acid metabolism and reducing inflammation, it can potentially counteract the damaging effects associated with bile imbalance linked to liver cancer.
What techniques are researchers using to explore bile acid metabolism in liver cancer?
Researchers are using a variety of techniques, including molecular and genomic approaches, to study the role of bile acid metabolism in liver cancer. These methods help uncover the mechanisms underlying liver diseases and potential treatment interventions.
Are there experimental models that support the link between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Yes, experimental models show that bile acid overproduction leads to liver damage and cancer progression. Studies indicate that activating FXR or inhibiting YAP can significantly reduce liver injury and cancer risks.
How does liver cancer treatment progress with the knowledge of bile acid dysregulation?
Knowledge of bile acid dysregulation is progressing liver cancer treatment by identifying new therapeutic targets, such as FXR, which can be stimulated to restore bile acid homeostasis and reduce liver cancer risks.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Critical imbalance in bile acids linked to liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. |
| YAP and FXR | YAP (Yes-associated protein) is identified as a repressor affecting bile acid metabolism by inhibiting FXR (Farnesoid X receptor). |
| Consequences of Imbalance | Overproduction of bile acids due to YAP activation leads to liver fibrosis, inflammation, and cancer progression. |
| Potential Treatments | Activation of FXR or inhibition of YAP’s repressor activity may provide therapeutic strategies for liver cancer treatment. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer is a pressing health concern linked to the regulation of bile acids produced by the liver. Recent research has unveiled a crucial molecular switch, namely YAP, that influences bile acid metabolism and promotes the progression of liver diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding and targeting these mechanisms may lead to innovative treatment options, highlighting the importance of ongoing studies in liver biology and cancer.